- Organic Chemistry
- Aldehydes and Ketones
- Alkyl Halides, Alcohols and ethers
- Amines and other nitrogen compounds
- Aromatic Chemistry
- Carbohydrates, Amino acids, protein, Vitamin and Fat
- Carboxylic acids and its derivatives
- Chemistry in daily life
- General Mechanism in organic compounds
- Hydrocarbons
- Nomenclature and isomerism
23 - Organic Chemistry Questions Answers
name of the compound CH3CH2CH2CH2NC
Primary alkyl halide C4H9Br (a) reacted with alcoholic KOH to give compound (b).Compound (b) is reacted with HBr to give (c) which is an isomer of (a). When (a) is reacted with sodium metal it gives compound (d), C8H18 which is different from the compound formed when n-butyl bromide is reacted with sodium. Give the structural formula of (a) and write the equations for all the reactions.
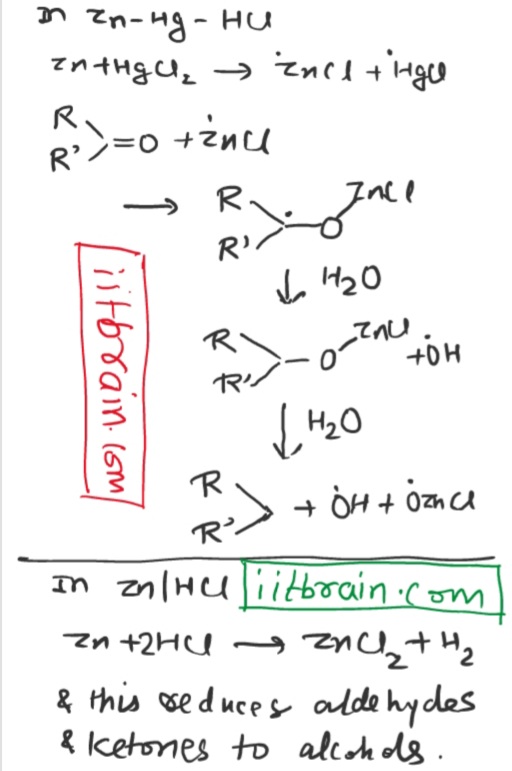
Why does
Zn + HCl reduce aldehydes and ketones to alcohols while
Zn - Hg amalgam + HCl reduce aldehyde and ketones to alkanes
H₂+ Pd + C Reagent ... It reduces a C=C to C-C ... Is this addition syn or anti?
It is syn reagent
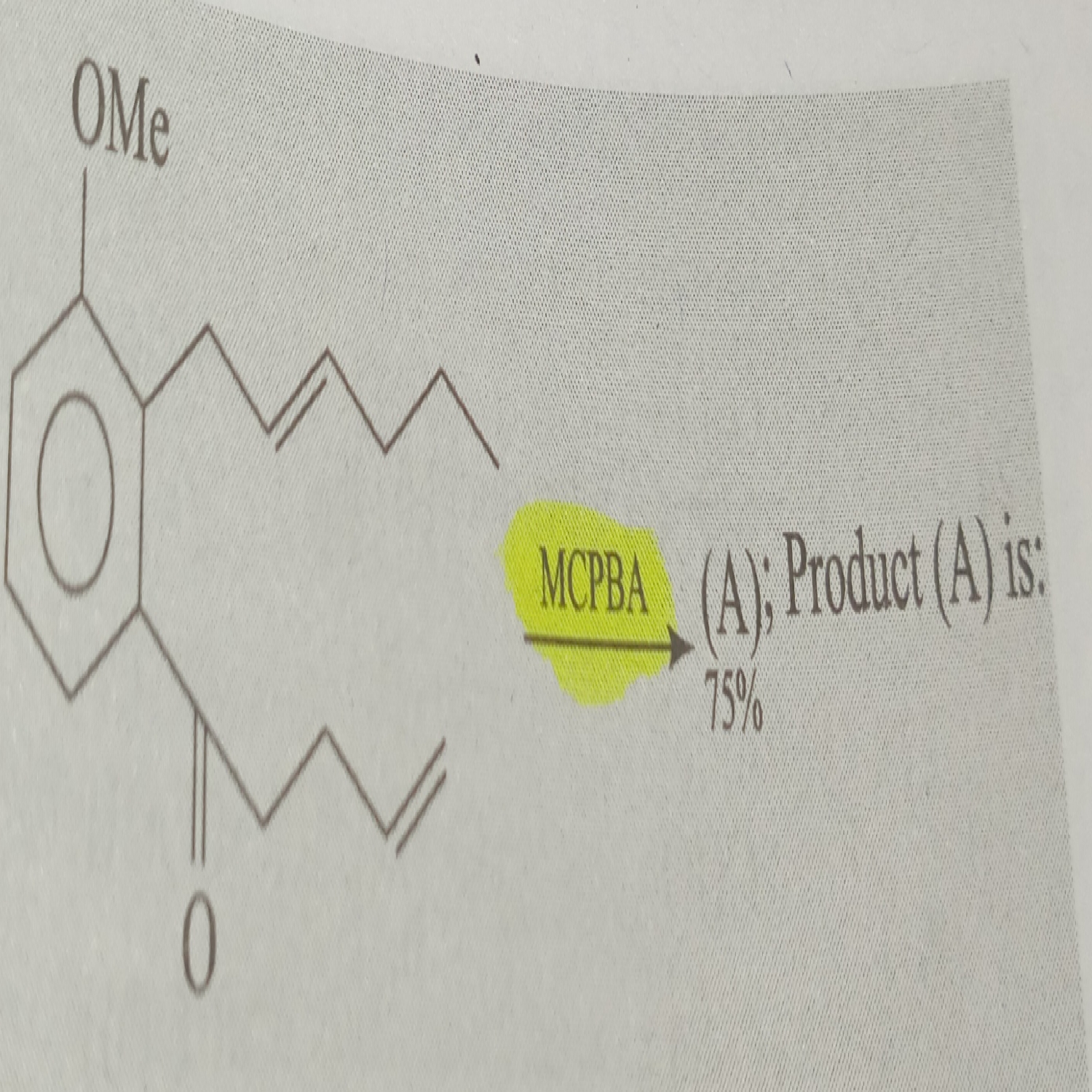
mCPBA is a good oxidizing agent for alkenes and ketones. Here both are present, in that case mCPBA attacks on alkene. Alkene on OMe side is more reactive. So make epoxide this side. Remember also that stereo nature is not changed in this reaction means cis be cis and trans be trans.
Is the H on B-carbon sterically hindered ?
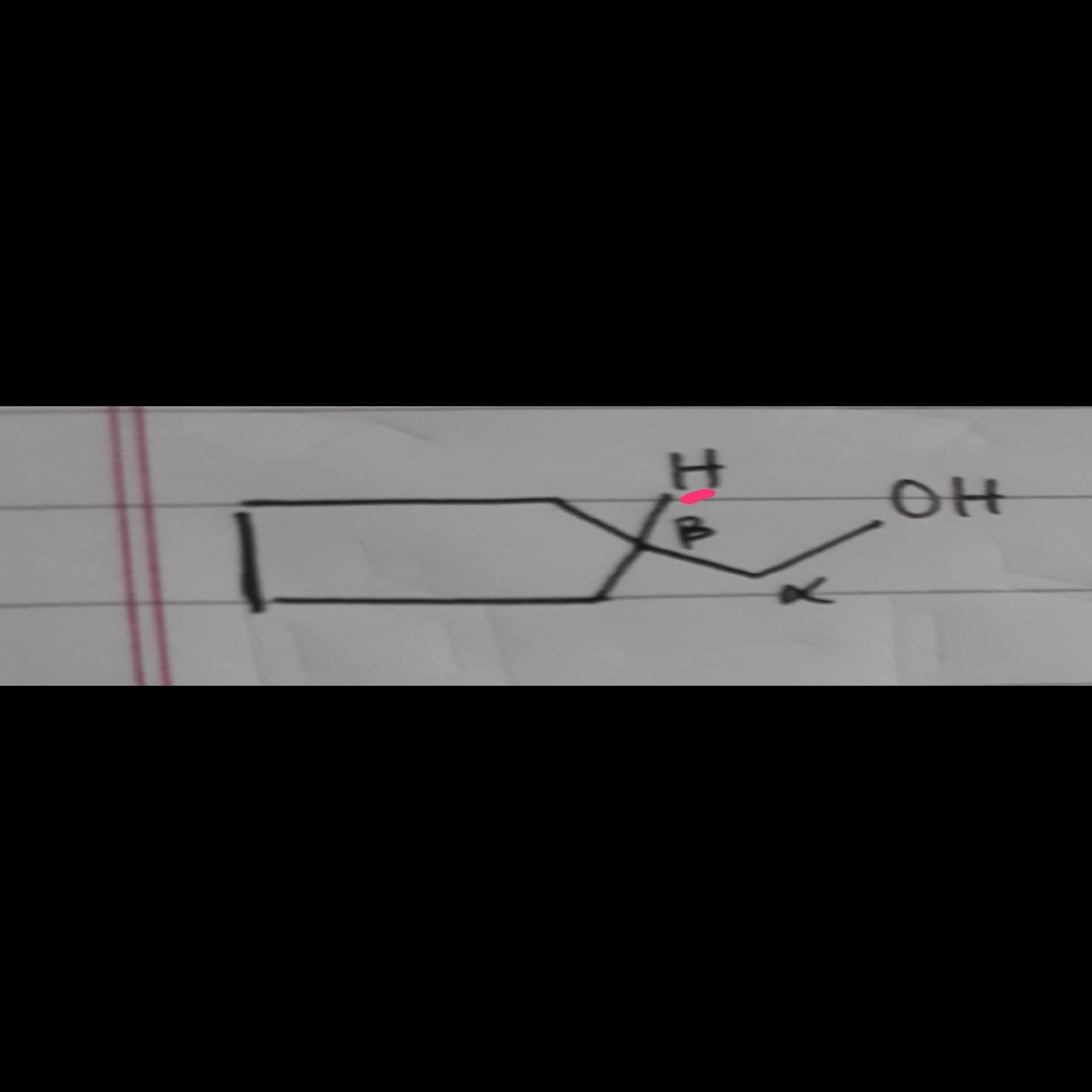
Steric hindrance is a relative word, so is compared between two carbons.
Tertiary carbon is always more sterically hindered than primary,
so β carbon is more hindered than α in this compound
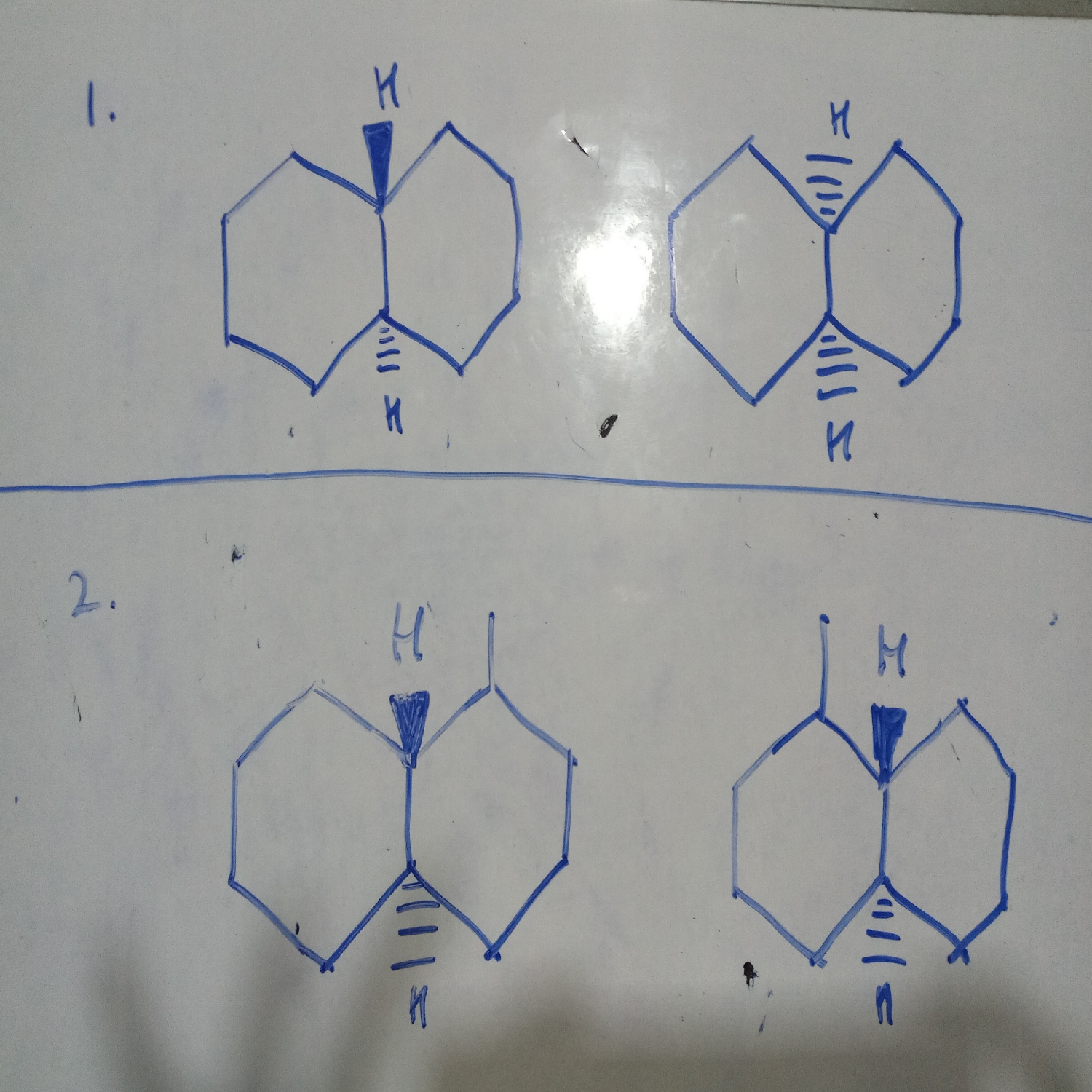
1. It is cis-trans pair (no chiral carbon atom so no optical isomerism)
2. has chiral carbon atom so case of optical isomerism, mirror images so dextro and laevo
CH3-(CHBr)-CH2-CH3 + Na --------> ?
in presence of ether it is Wurtz reaction and as obvious many products will be formed.
Major product will be CH3-CH2-CH(CH3)-CH(CH3)-CH2-CH3