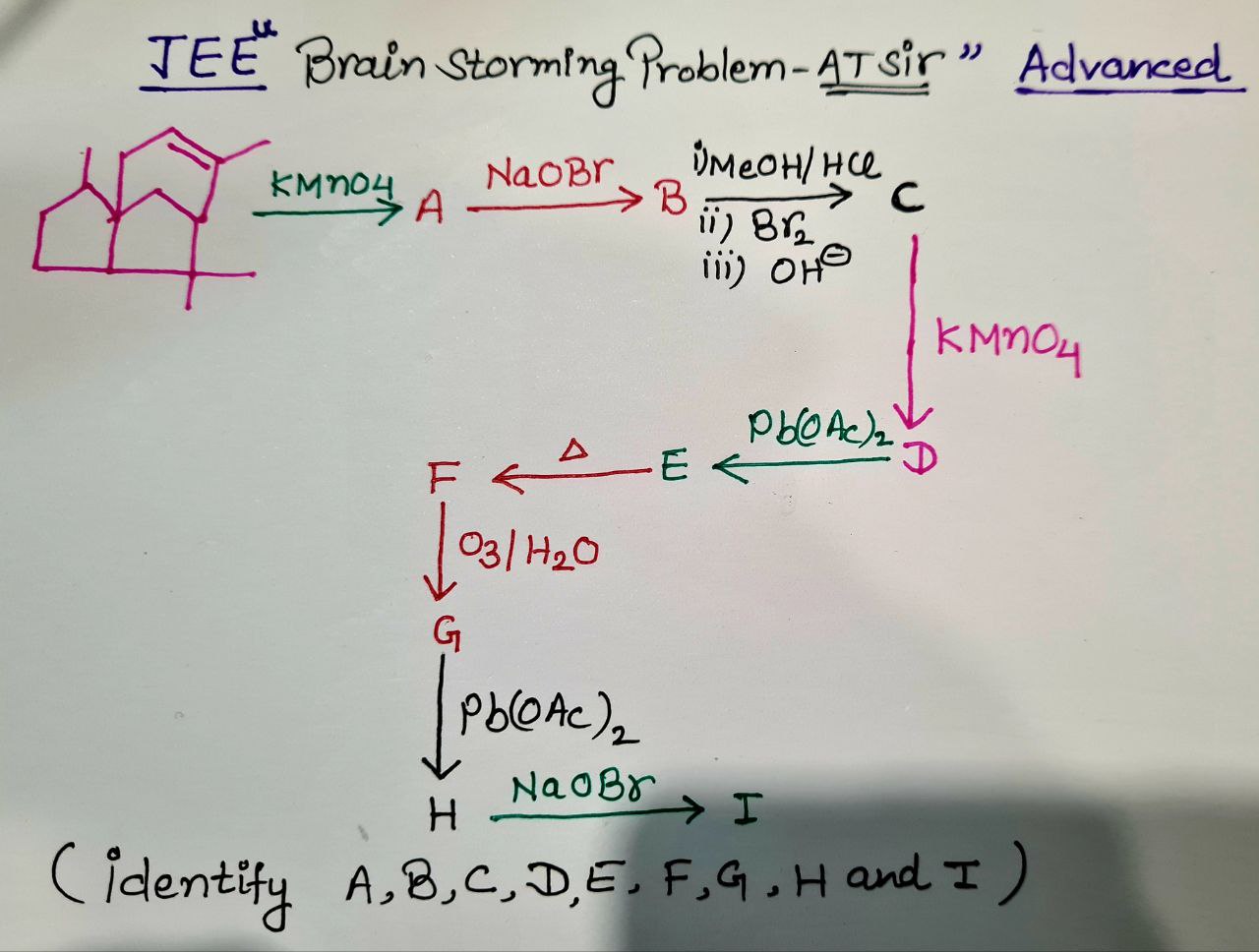
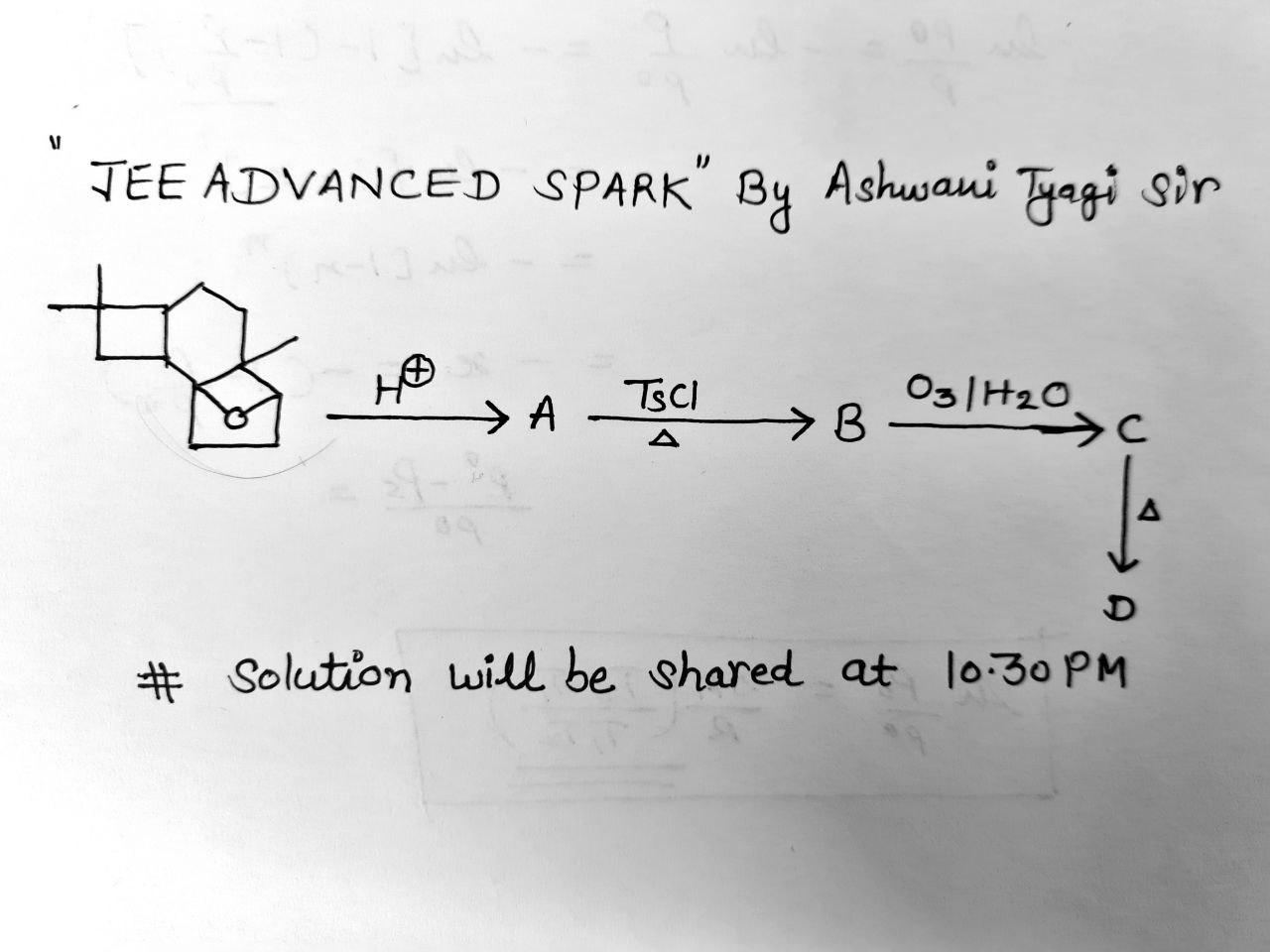
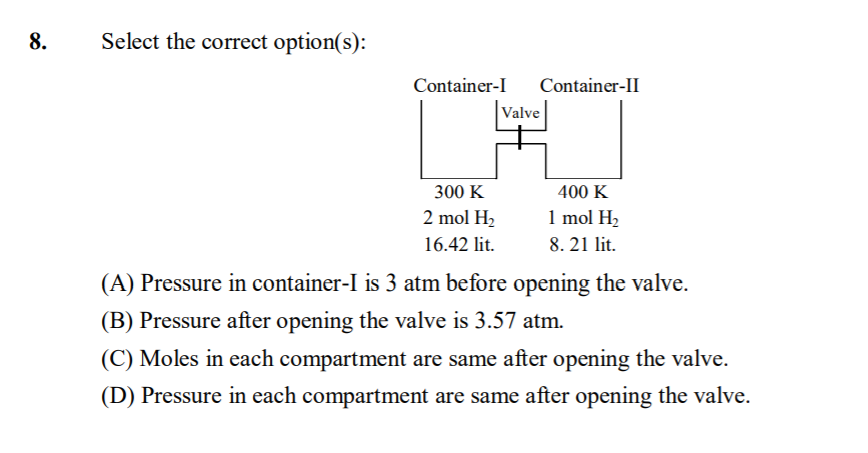
- Organic Chemistry
- Aldehydes and Ketones
- Alkyl Halides, Alcohols and ethers
- Amines and other nitrogen compounds
- Aromatic Chemistry
- Carbohydrates, Amino acids, protein, Vitamin and Fat
- Carboxylic acids and its derivatives
- Chemistry in daily life
- General Mechanism in organic compounds
- Hydrocarbons
- Nomenclature and isomerism
217 - Chemistry Questions Answers
I want this account closed. I just had to open an account but it’s showing up as a breach to my email. I want an email stating the account has been closed
name of the compound CH3CH2CH2CH2NC
Primary alkyl halide C4H9Br (a) reacted with alcoholic KOH to give compound (b).Compound (b) is reacted with HBr to give (c) which is an isomer of (a). When (a) is reacted with sodium metal it gives compound (d), C8H18 which is different from the compound formed when n-butyl bromide is reacted with sodium. Give the structural formula of (a) and write the equations for all the reactions.

Joshi sir comment
Constant b is associated to volume correction so its value be less for molecule of smaller volume.
What is the driving force for the reaction
F₂ + H₂O -> H₂F₂ + O₂
Is the very low bond energy of F₂?
Considering the electrode potential of hydrogen to be zero, electrode potential of fluorine is +2.87 volt. It implies that fluorine is best oxidising agent, and thus it oxidises oxygen in the given reaction. Besides it low bond energy of fluorine is also a factor for its dissociation and participation in the reaction.

Amount of DCl = 4 milimole
Amount of NaOD = 8 milimole
After reaction of acid and base
Amount of NaOD remaining = 4 milimole
Total volume = 100 ml = 0.1 lit
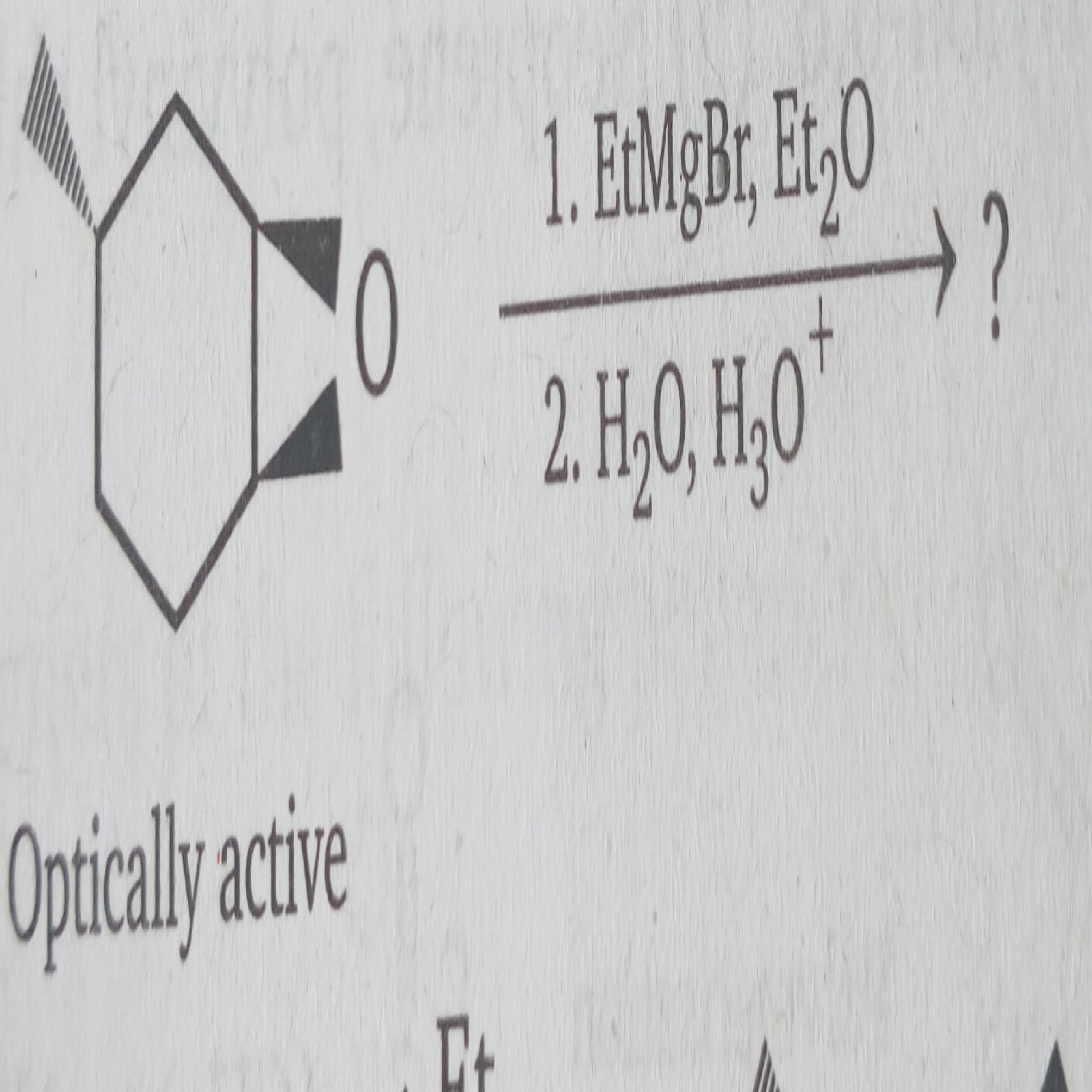
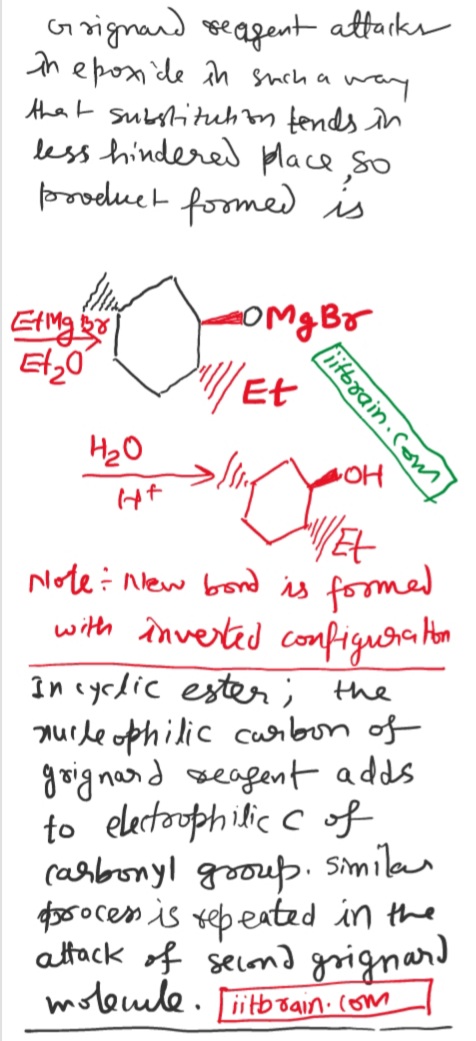
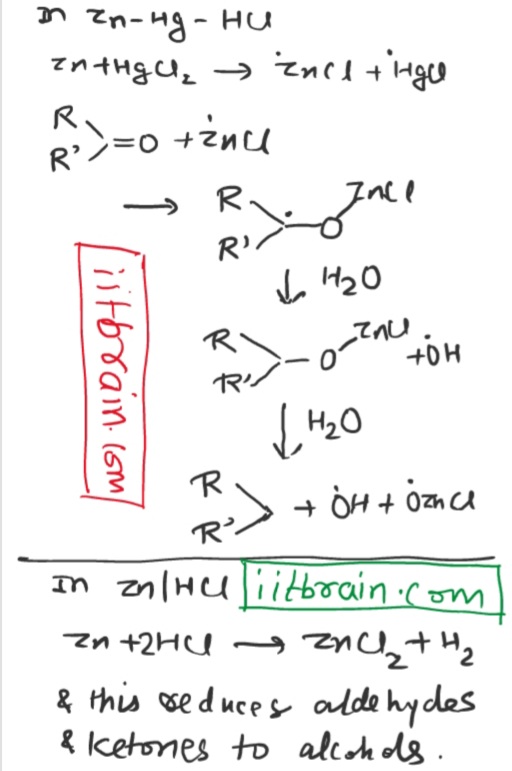
Why does
Zn + HCl reduce aldehydes and ketones to alcohols while
Zn - Hg amalgam + HCl reduce aldehyde and ketones to alkanes