- Organic Chemistry
- Aldehydes and Ketones
- Alkyl Halides, Alcohols and ethers
- Amines and other nitrogen compounds
- Aromatic Chemistry
- Carbohydrates, Amino acids, protein, Vitamin and Fat
- Carboxylic acids and its derivatives
- Chemistry in daily life
- General Mechanism in organic compounds
- Hydrocarbons
- Nomenclature and isomerism
217 - Chemistry Questions Answers
H₂+ Pd + C Reagent ... It reduces a C=C to C-C ... Is this addition syn or anti?
It is syn reagent
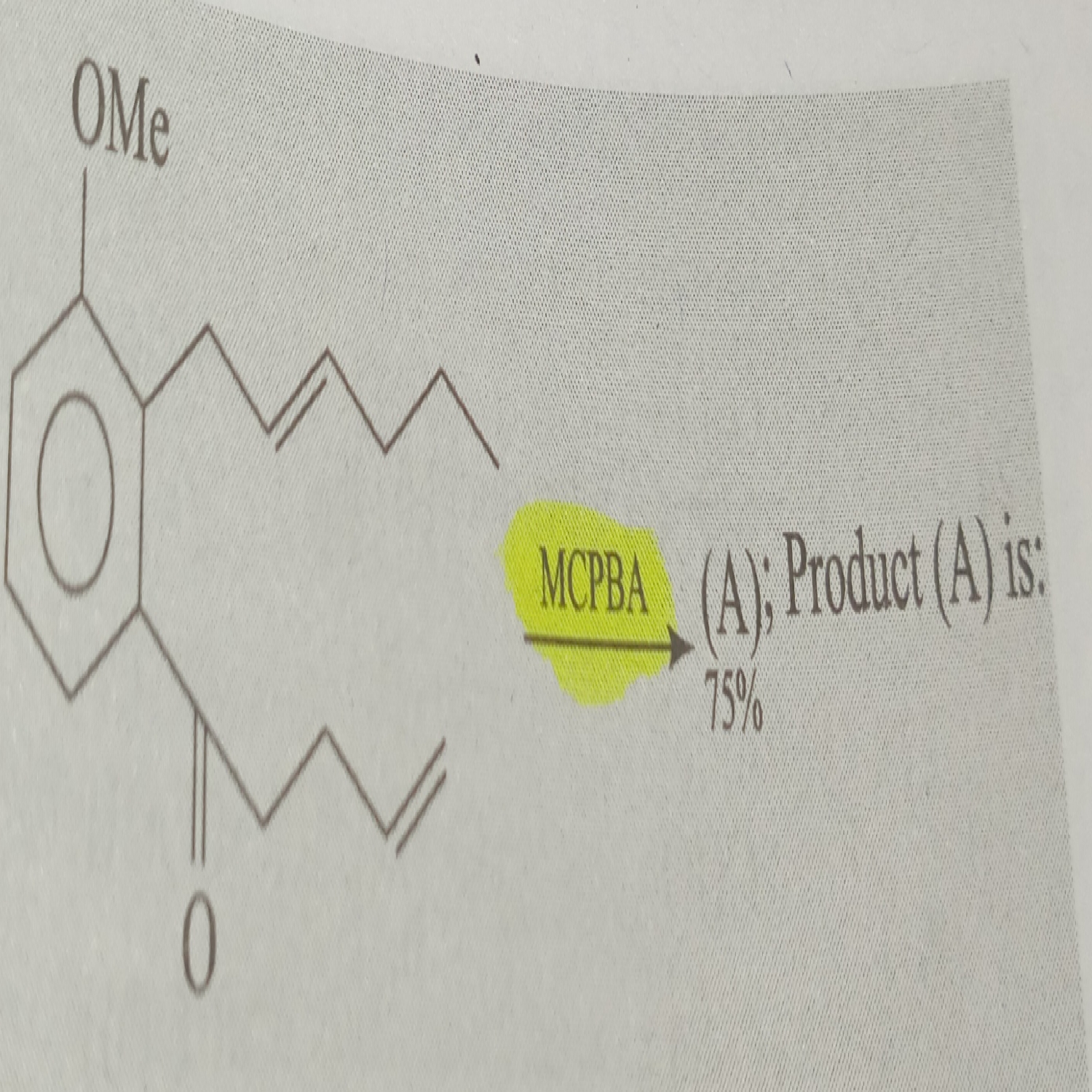
mCPBA is a good oxidizing agent for alkenes and ketones. Here both are present, in that case mCPBA attacks on alkene. Alkene on OMe side is more reactive. So make epoxide this side. Remember also that stereo nature is not changed in this reaction means cis be cis and trans be trans.
Does stabilization of a charge mean willingness of other atoms in the molecule to share the charge or the extent of sharing of charge ? If its the 1st then how does that stabilize the charge?
Sharing is the case applicable for the atoms of same electronegativity, thus by sharing electrons (charges) atoms make their orbital configurations stable according to the rules defined for stability.
Is the H on B-carbon sterically hindered ?
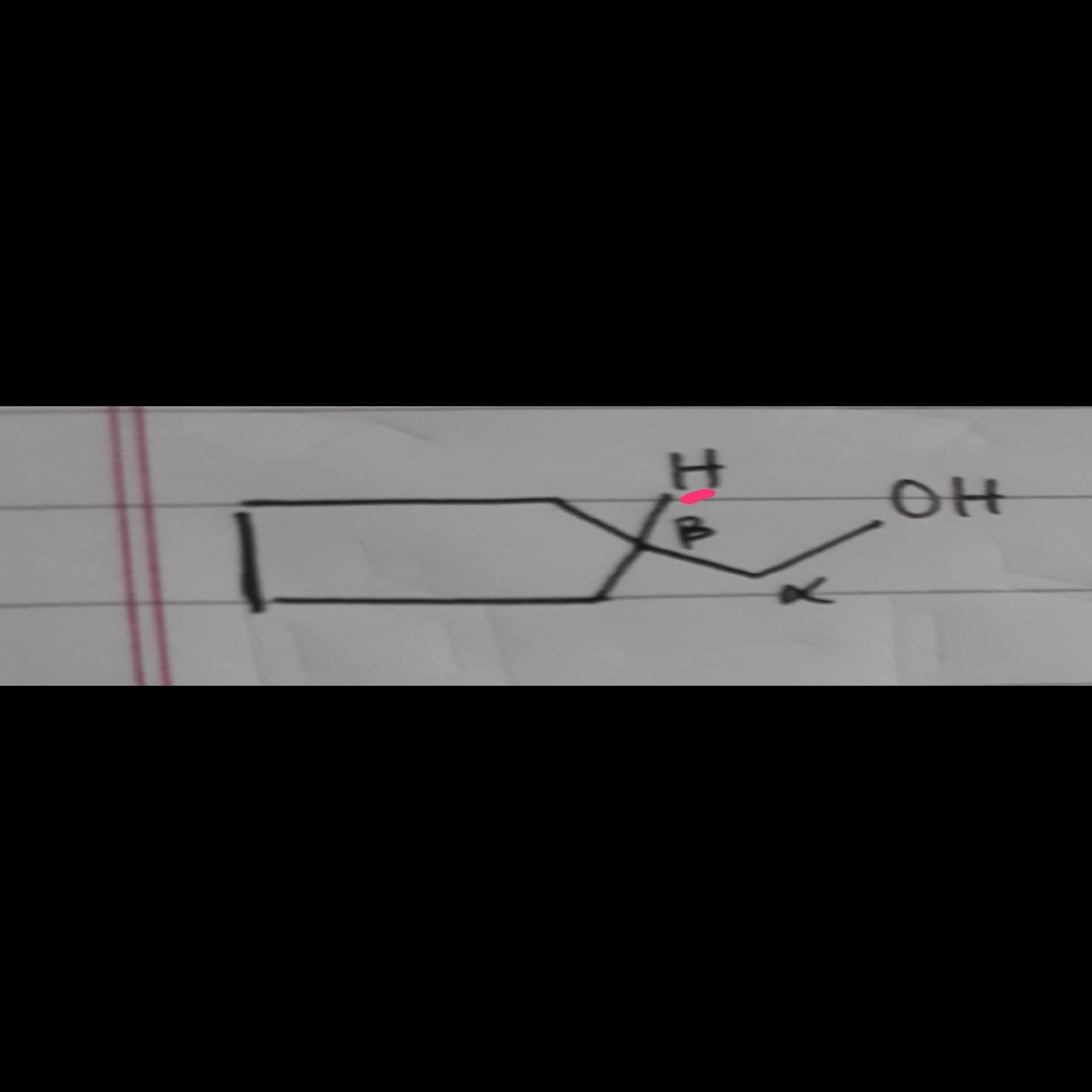
Steric hindrance is a relative word, so is compared between two carbons.
Tertiary carbon is always more sterically hindered than primary,
so β carbon is more hindered than α in this compound


In first case reactions involved areReduction of Fe+++, Fe+++→Fe++Titration step, 6Fe+++K2Cr2O7→6Fe++++2Cr+++By using titration reaction, solve the question
In second case reaction involved isAs4O6+4I3-→As4O10+12I-Now solve
inform if any issue
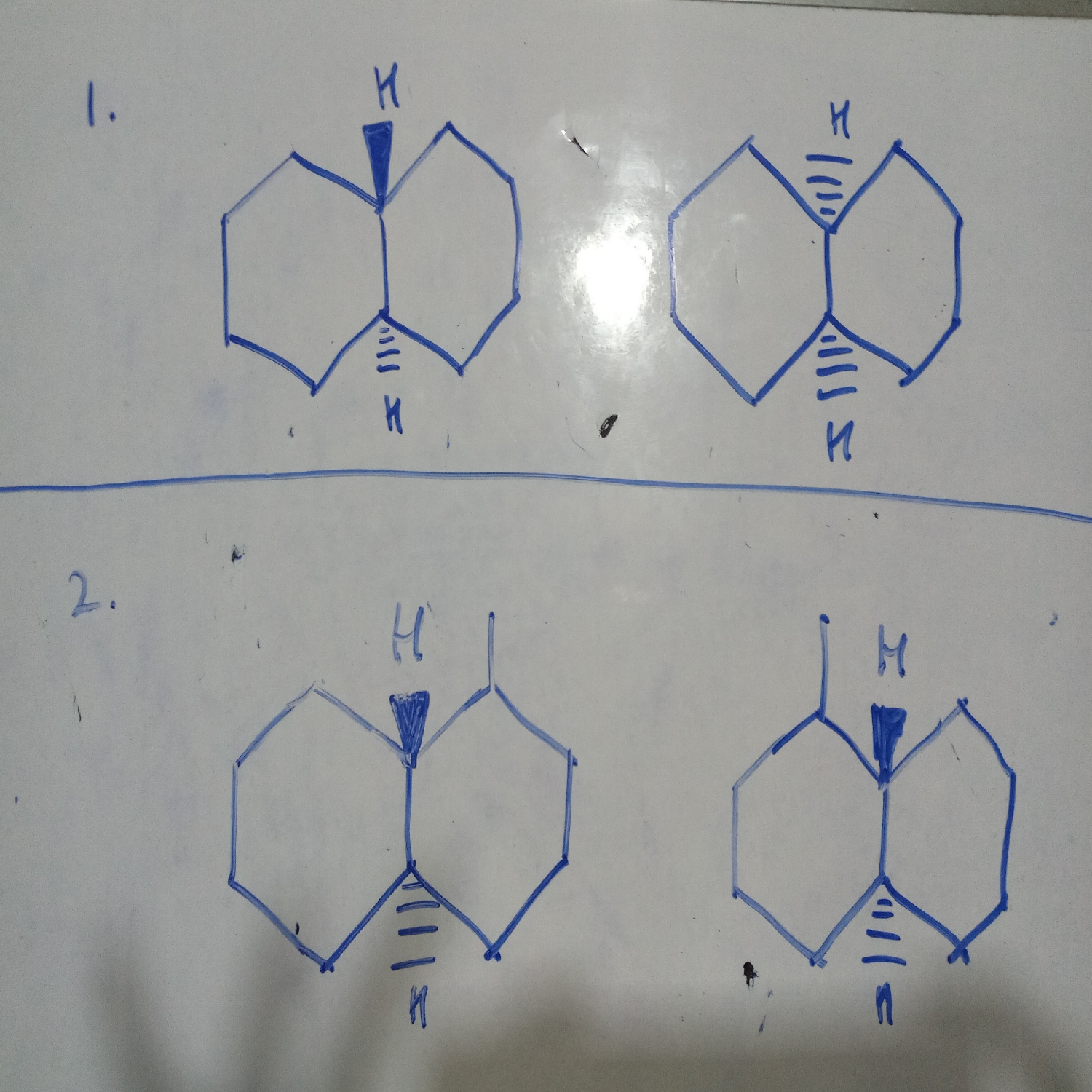
1. It is cis-trans pair (no chiral carbon atom so no optical isomerism)
2. has chiral carbon atom so case of optical isomerism, mirror images so dextro and laevo
Balance
KMnO4+H2SO4+H2S -> K2SO4+MnSO4+S+H2O
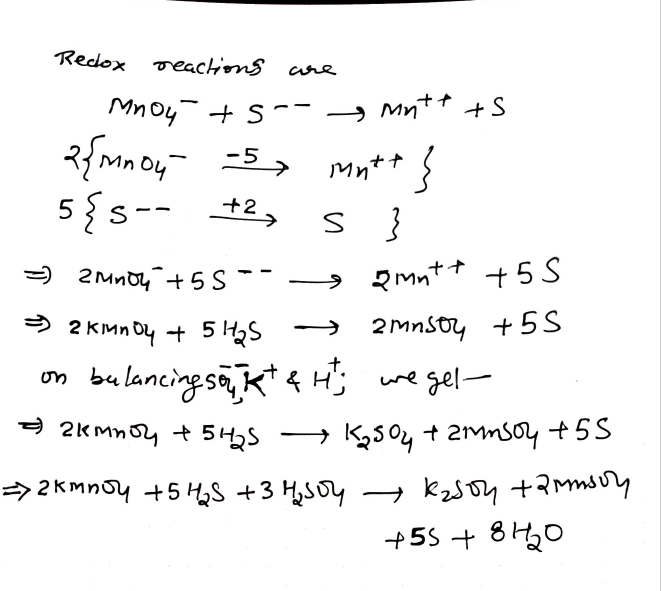
Q.WRITE CELL RECTION OF THE FOLLOWING- .{1} ZN | ZN2+ || cu2+ |cu {2} PT {H2} | HCL || CL2{PT}
Zn -----------> Zn++ + 2e-
Cu++ + 2e- -----------> Cu
H2 --------> 2H+ + 2e-
Cl2 + 2e- --------> 2Cl-
If each orbital can hold a maximum of three electrons , then the number of elements in 9th period of periodic table
3/2 times of the previous number of elements
At 752 mm Hg of total Pressure and 301 K Temperature 150 ml H2 is produced and collected over the water, when current is passed through acidic water for 1 hour. How many Amp. current should have passed? ( at 301 K temperature, The pressure of water is 28 mm Hg )
A) 0.320 A
B) 310 A
C) 321 A
D) 0.305 A
please mention correct answer.
by formula PV/T = constant
(752-28)*150/301 = 760*V/273
solve for V, this will be the equivalent volume at STP
now convert this volume in gm by the formula 2V/22400
then finally m = zit, where
z = 1/96500
solve it for i
