6 - Applications of integrations Questions Answers

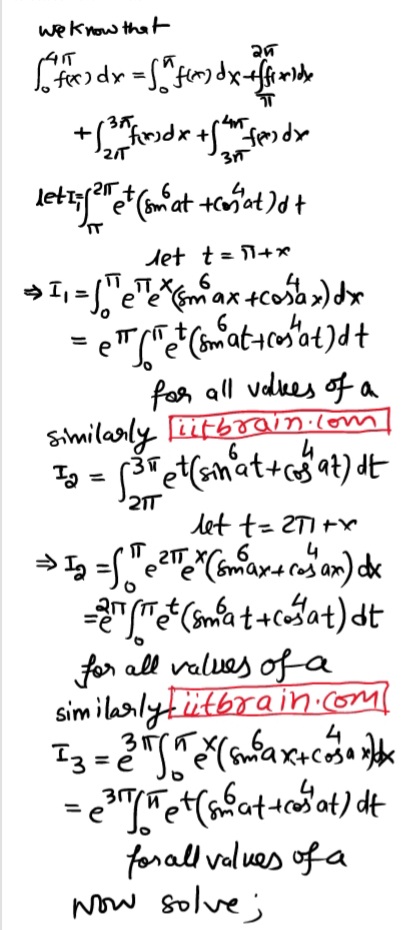
y=px+a/p
this is a special type of differential equation in which p = dy/dx
its solution will be y = cx+(a/c) here c is a constant
y-xp=x+yp
on applying p = dy/dx
(ydx-xdy)/dx = (xdx+ydy)/dx
or ydx-xdy = xdx+ydy
or dy/dx = (y-x)/(y+x)
now it is homogeneous
A function f : R® R satisfies f(x+y) = f(x) + f(y) for all x,y Î R and is continuous throughout the domain. If I1 + I2 + I3 + I4 + I5 = 450, where In = n.0òn f(x) dx. Find f(x).
according to the given condition f(nx) = n f(x)
0òn f(x) dx
consider x = ny so this integration will become 0ò1 f(ny) ndy = n2 0ò1 f(y) dy = n2 0ò1 f(x) dx
now by using these conditions I1 = 13 0ò1 f(x) dx similarly others
put these values and get the answer
Show that 0òp q3 ln sin q dq = 3p/2 0òp q2 ln [Ö2 sin q] dq.
let I = 0òp q ln sin q dq
on aplying property of definite integral
I = 0òp (π-q) ln sin q dq
so 2 I = 0òp π ln sin q dq
or I = π/2 0òp ln sin q dq
or I = 2π/2 0òp/2 ln sin q dq this is due to property
similarly solve 0òp q2 ln sin q dq and then 0òp q3 ln sin q dq
finally solve the right hand side of the equation to prove LHS = RHS
Let g(x) be a continuous function such that 0ò1 g(t) dt = 2. Let f(x) = 1/2 0òx (x-t)2 g(t) dt then find f '(x) and hence evaluate f "(x).
f(x) = 1/2 0òx (x-t)2 g(t) dt
or f(x) = 1/2 0òx x2 g(t) dt + 1/2 0òx t2 g(t) dt - 0òx x t g(t) dt
or f(x) = 1/2 x2 0òx g(t) dt + 1/2 0òx t2 g(t) dt - x 0òx t g(t) dt
now use newton leibniz formula for middle function and product rule for first and last functions for finding f' (x)
similarly get f'' (x)
